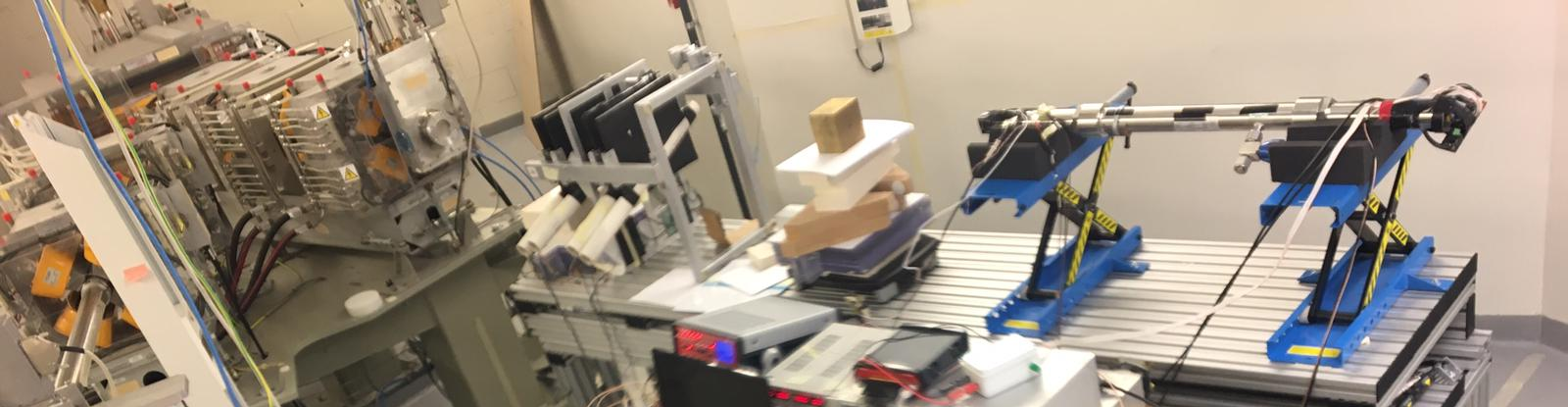
ADHD - Anti Deuteron Helium Detector
The observation of GeV and sub-GeV anti-deuteron in the cosmic ray flux, could be a very strong signature of dark matter annihilation in our galaxy. Goal of the Anti Deuteron Helium Detector (ADHD) project is to study the signatures offered by an high pressure He target for the identification of antideuterons in space.
The Science
The theoretically predicted antideuteron flux resulting from secondary interactions of primary cosmic rays with the Inter-Stellar medium is expected to be very low and in particular is kinematically suppressed at low energy (sub-GeV).
Well motivated theories beyond the Standard Model contain viable dark matter candidates, which could lead to a significant enhancement of the antideuteron flux due to annihilation or decay of dark matter particles. This flux contribution is believed to be relatively large at low energies, where the secondary background is suppressed, which leads to an high interest in the development of new detection signatures for low energy antideuteron.
Goal of the Anti Deuteron Helium Detector (ADHD) project is to study the signatures offered by an high pressure He target for the identification of antideuterons in space. In particular exotic atoms are produced by stopping antiprotons/antideuterons in helium gas.
The antiparticle spontaneously removes one of the two electrons contained in a normal helium atom, then begins to orbit the helium nucleus in the electron's place but with large principal and angular momentum quantum numbers. The antideuteron's orbit then lies far away from the surface of the helium nucleus inhibiting the annihilation. This is expected to happens in the case of few percent of the captures. For the He target, the single existing electron cannot provide (fast) Auger de-excitation channels, moreover it prevents also the Stark collisional de-excitation, thus, the (slow) radiative process is the main de-excitation channel. This meta-stability is an unique (and well measured) feature for the He target that is not expected/observed for other target nuclei.
The captured antideuteron can thus orbit the He nucleus for tens of microseconds, before finally falling to its surface and annihilating providing a few charged pion tracks. This characteristic delayed annihilation signal in He is a distinctive signature to identify the antimatter nature of the stopping particle.
Existing antiproton background can be separated from the antideuteron signal thanks to the half pion multiplicity and velocity vs kinetic energy measurement. A prototype based on the ARKTIS B470 (200bar) Helium scintillator will be developed at TIFPA and tested at the TIFPA-managed experimental proton beam of the Trento Protontherapy Centre.
TEAM
• Involved external institutions: ARKTIS
• INFN groups: TIFPA
• Principal Investigator: Francesco Nozzoli, TIFPA
• INFN Project: CSN II
• Duration: 3 years (2019-2021)
TIFPA Team
• Local responsible for TIFPA:
 | Francesco Nozzoli |
• Involved TIFPA people:
 | Francesco Dimiccoli | |
 | Roberto Iuppa | |
 | Ignazio Lazzizzera | |
 | Ester Ricci | |
 | Paolo Zuccon |
External resources
ADHD slides at "Antideuteron 2019" - UCLA - Los Angeles
Cosmic-ray antinuclei as messengers of new physics: status and outlook for the new decade JCAP 08 (2020) 035
Perspectives of dark matter indirect search with ADHD in space J.Phys.Conf.Ser. 1548 (2020) 012035
Detectors for antideuteron search in cosmic rays: current status and new ideas JINST 15 (2020) C06033
Images
Click on the image to see an enlarged version
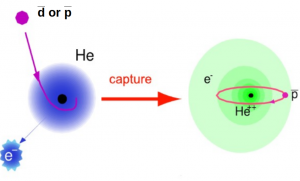
Stopping antiprotons and antideuterons (but also π- and k-) are captured by He and trapped in (μs living) meta-stable states before annihilation. Meta-stable states exists only for He target.
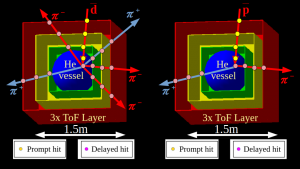
The ADHD detector is made by a 400 bar He gas calorimeter (HeCal) contained in a spherical light thermoplastic vessel, inside three layers of fast scintillator (ToF). Antiprotons and antideuterons produce a single in-going prompt track followed by many out-going delayed tracks. Antideuteron's annihilations produce twice the number of delayed out-going tracks with respect to antiproton's annihilations.
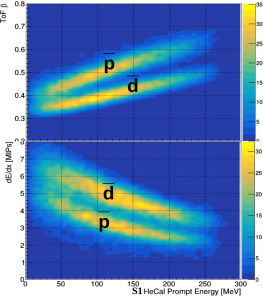
The antideuterons can be separated from antiprotons thanks to the comparison of prompt track velocity and energy loss as measured by ToF with the total kinetic energy as measured by HeCal (S1).
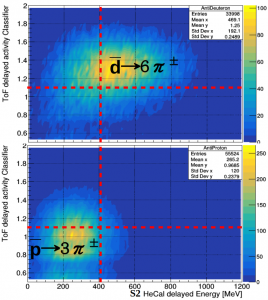
Antideuterons can be separated from antiprotons also thanks to the number/energy of delayed hits in ToF and the delayed energy measured by HeCal (S2). Combining prompt and delayed event information ADHD is able to measure 1 antideuteron over 1000 background antiprotons in the 50-150 MeV/n range.
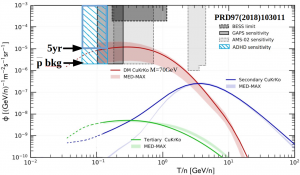
Expected ADHD sensitivity to antideuteron flux compared with theoretical Dark Matter and secondary background models. ADHD has sensitivity similar to the ones expected from AMS-02 and GAPS but in a complementary energy region. ADHD would provide also new antiproton flux measurements in the 100-300 MeV energy region with few % error.

The SiPM ring array developed at TIFPA. The particles can enter in the HeCal detector avoiding to cross the sensitive photodetector surface.




